你知道胎儿在子宫里可以尿尿吗?B超师捕捉到一个男宝宝在妈妈的肚子里滋滋的尿起来,真是神奇的生命啊
Category Archives: Flutter学习交流
flutter环境更新方法
常规更新方法:
运行:flutter upgrade,然后等待自动更新完成即可,
非常贵更新方法:
1.更新flutter代码库
找到flutter库的安装目录,运行git,同步拉取到最新的代码,
2.更新依赖
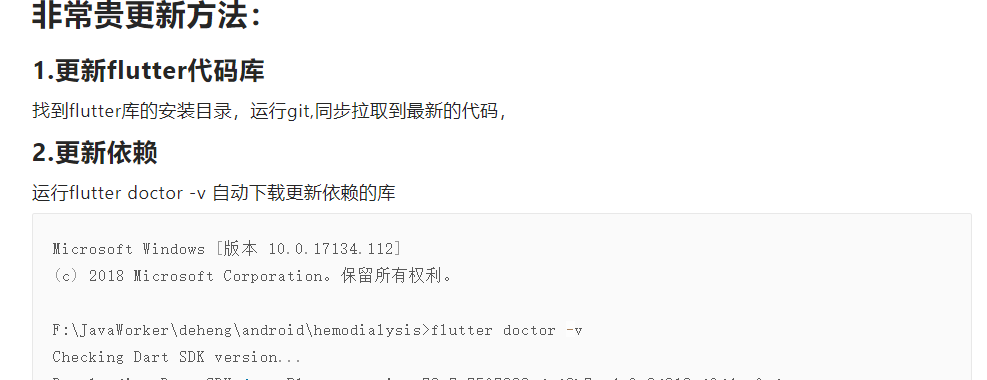
运行flutter doctor -v 自动下载更新依赖的库
Microsoft Windows [版本 10.0.17134.112]
(c) 2018 Microsoft Corporation。保留所有权利。
F:\JavaWorker\deheng\android\hemodialysis>flutter doctor -v
Checking Dart SDK version...
Downloading Dart SDK from Flutter engine 72c7a7567228cdaf8b7aa4a9e3d212ef9d4cc0ed...
Unzipping Dart SDK...
Building flutter tool...
Running pub upgrade...
Downloading package sky_engine... 1.1s
Downloading common tools... 2.6s
Downloading windows-x64 tools... 5.9s
Downloading android-arm-profile/windows-x64 tools... 1.2s
Downloading android-arm-release/windows-x64 tools... 0.8s
Downloading android-arm64-profile/windows-x64 tools... 0.9s
Downloading android-arm64-release/windows-x64 tools... 0.9s
Downloading android-x86 tools... 4.8s
Downloading android-x64 tools... 4.9s
Downloading android-arm tools... 3.4s
Downloading android-arm-profile tools... 1.8s
Downloading android-arm-release tools... 2.2s
Downloading android-arm64 tools... 1.9s
Downloading android-arm64-profile tools... 1.8s
Downloading android-arm64-release tools... 1.5s
Downloading android-arm-dynamic-profile tools... 1.9s
Downloading android-arm-dynamic-release tools... 2.8s
Downloading android-arm64-dynamic-profile tools... 2.0s
Downloading android-arm64-dynamic-release tools... 1.7s
[√] Flutter (Channel beta, v0.10.3-pre.3, on Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.17134.112], locale zh-CN)
• Flutter version 0.10.3-pre.3 at F:\ProgramFiles\flutter
• Framework revision 233435c02a (42 minutes ago), 2018-11-30 10:00:27 +0800
• Engine revision 72c7a75672
• Dart version 2.1.0 (build 2.1.0-dev.9.4 f9ebf21297)
[√] Android toolchain - develop for Android devices (Android SDK 28.0.3)
• Android SDK at F:\ProgramFiles\android\sdk
• Android NDK location not configured (optional; useful for native profiling support)
• Platform android-28, build-tools 28.0.3
• ANDROID_HOME = F:\ProgramFiles\android\sdk
• Java binary at: F:\ProgramFiles\android\Android Studio\jre\bin\java
• Java version OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_152-release-1136-b06)
• All Android licenses accepted.
[√] Android Studio (version 3.2)
• Android Studio at F:\ProgramFiles\android\Android Studio
• Flutter plugin version 31.1.1
• Dart plugin version 181.5656
• Java version OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_152-release-1136-b06)
[√] IntelliJ IDEA Ultimate Edition (version 2018.2)
• IntelliJ at F:\ProgramFiles\JetBrains\IntelliJ IDEA 2018.2.4
• Flutter plugin version 30.0.2
• Dart plugin version 182.5124
[√] Connected device (2 available)
• MI PAD 4 • 6074f4a0 • android-arm64 • Android 8.1.0 (API 27)
• Che1 CL20 • f4e3fb7f933b • android-arm • Android 4.4.4 (API 19)
• No issues found!
F:\JavaWorker\deheng\android\hemodialysis>
You need to add a widget, row, or prebuilt layout before you’ll see anything here. 🙂
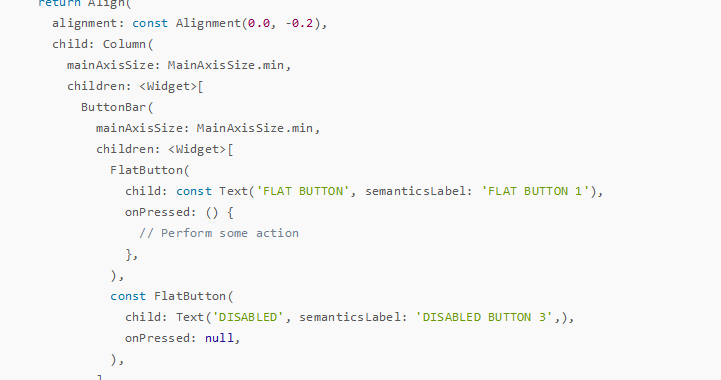
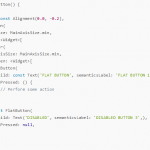
按钮扁平化用法示例-buildFlatButton
Widget buildFlatButton() {
return Align(
alignment: const Alignment(0.0, -0.2),
child: Column(
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.min,
children: <Widget>[
ButtonBar(
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.min,
children: <Widget>[
FlatButton(
child: const Text('FLAT BUTTON', semanticsLabel: 'FLAT BUTTON 1'),
onPressed: () {
// Perform some action
},
),
const FlatButton(
child: Text('DISABLED', semanticsLabel: 'DISABLED BUTTON 3',),
onPressed: null,
),
],
),
ButtonBar(
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.min,
children: <Widget>[
FlatButton.icon(
icon: const Icon(Icons.add_circle_outline, size: 18.0),
label: const Text('FLAT BUTTON', semanticsLabel: 'FLAT BUTTON 2'),
onPressed: () {
// Perform some action
},
),
FlatButton.icon(
icon: const Icon(Icons.add_circle_outline, size: 18.0),
label: const Text('DISABLED', semanticsLabel: 'DISABLED BUTTON 4'),
onPressed: null,
),
],
),
],
),
);
}
factory FlatButton.icon({
Key key,
@required VoidCallback onPressed,
ValueChanged<bool> onHighlightChanged,
ButtonTextTheme textTheme,
Color textColor,
Color disabledTextColor,
Color color,
Color disabledColor,
Color highlightColor,
Color splashColor,
Brightness colorBrightness,
EdgeInsetsGeometry padding,
ShapeBorder shape,
Clip clipBehavior,
MaterialTapTargetSize materialTapTargetSize,
@required Widget icon,
@required Widget label,
}) = _FlatButtonWithIcon;
const FlatButton({
Key key,
@required VoidCallback onPressed,
ValueChanged<bool> onHighlightChanged,
ButtonTextTheme textTheme,
Color textColor,
Color disabledTextColor,
Color color,
Color disabledColor,
Color highlightColor,
Color splashColor,
Brightness colorBrightness,
EdgeInsetsGeometry padding,
ShapeBorder shape,
Clip clipBehavior = Clip.none,
MaterialTapTargetSize materialTapTargetSize,
@required Widget child,
}) : super(
key: key,
onPressed: onPressed,
onHighlightChanged: onHighlightChanged,
textTheme: textTheme,
textColor: textColor,
disabledTextColor: disabledTextColor,
color: color,
disabledColor: disabledColor,
highlightColor: highlightColor,
splashColor: splashColor,
colorBrightness: colorBrightness,
padding: padding,
shape: shape,
clipBehavior: clipBehavior,
materialTapTargetSize: materialTapTargetSize,
child: child,
);
7 of 7 in the series: Fltter移动开发相关
- sqflite操作相关

- TextField多行操作

- 免费作图工具

- Flutter环境更新方法
- 实体类自动生成工具的配置
实体类自动生成工具的配置
- 理解Flutter widget的生命周期
- 按钮扁平化用法示例-buildFlatButton
按钮扁平化用法示例-buildFlatButton
免费作图工具
本页收集一些免费的工具,创建漂亮的图表。
ProcessOn
在线版:https://www.processon.com/

yEd
桌面版:https://www.yworks.com/products/yed
在线版:https://www.yworks.com/products/yed-live

Pencil

Dia

Inkscape

Draw.io
桌面版:https://about.draw.io/integrations/#integrations_offline

Whimsical

PlantUML
在线版:http://www.plantuml.com/plantuml/

迅捷画图
在线版:https://www.liuchengtu.com/

百度脑图

Visual Paradigm Online
在线版:https://online.visual-paradigm.com

Creately

Coggle

3 of 7 in the series: Fltter移动开发相关
- sqflite操作相关

- TextField多行操作

- 免费作图工具

- Flutter环境更新方法
- 实体类自动生成工具的配置

实体类自动生成工具的配置
- 理解Flutter widget的生命周期

- 按钮扁平化用法示例-buildFlatButton

按钮扁平化用法示例-buildFlatButton
理解Flutter widget的生命周期
前言:
生命周期是一个组件加载到卸载的整个周期,熟悉生命周期可以让我们在合适的时机做该做的事情,
flutter中的State生命周期和android以及React Native的生命周期类似。
flutter中的State生命周期和android以及React Native的生命周期类似。
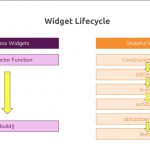
生命周期的流程图:
大致可以分为3个阶段:
初始化
State初始化时会依次执行 : 构造函数 > initState > didChangeDependencies > Widget build , 此时页面加载完成。
然后我们看一下每个函数的意义:
构造函数
调用次数:1次
这个函数严格意义上来讲不属于生命周期的一部分,因为这个时候State的widget属性为空,无法在构造函数中访问widget的属性 。但是构造函数必然是要第一个调用的。可以在这一部分接收前一个页面传递过来的数据。
initState
Called when this object is inserted into the tree.
调用次数:1次
当插入渲染树的时候调用,这个函数在生命周期中只调用一次。这里可以做一些初始化工作,比如初始化State的变量。
didChangeDependencies
Called when a dependency of this [State] object changes.
初始化时,在initState()之后立刻调用
当依赖的InheritedWidget rebuild,会触发此接口被调用
这个函数会紧跟在initState之后调用,并且可以调用BuildContext.inheritFromWidgetOfExactType,那么BuildContext.inheritFromWidgetOfExactType的使用场景是什么呢?最经典的应用场景是
new DefaultTabController(length: 3, child: new TabBar(
tabs: [ "主页","订单","我的" ]
.map( (data)=>new Text(data) ).toList(),
TabBar本来需要定义一个TabController,但是在外面套一层DefaultTabController就不需要定义TabContrller了,看下源码:
@override
void didChangeDependencies() {
super.didChangeDependencies();
_updateTabController();
_initIndicatorPainter();
}
void _updateTabController() {
final TabController newController = widget.controller ?? DefaultTabController.of(context);
...
}
注意到这里DefaultTabController.of(context)
static TabController of(BuildContext context) {
final _TabControllerScope scope = context.inheritFromWidgetOfExactType(_TabControllerScope);
return scope?.controller;
}
实际上就是调用BuildContext.inheritFromWidgetOfExactType,也就说在didChangeDependencies中,可以跨组件拿到数据。
运行时
build
调用次数:多次
初始化之后开始绘制界面,当setState触发的时候会再次被调用
didUpdateWidget
Called whenever the widget configuration changes.
祖先节点rebuild widget时调用 .当组件的状态改变的时候就会调用didUpdateWidget.
理论上setState的时候会调用,但我实际操作的时候发现只是做setState的操作的时候没有调用这个方法。而在我改变代码hot reload时候会调用 didUpdateWidget 并执行 build…
实际上这里flutter框架会创建一个新的Widget,绑定本State,并在这个函数中传递老的Widget。
这个函数一般用于比较新、老Widget,看看哪些属性改变了,并对State做一些调整。
需要注意的是,涉及到controller的变更,需要在这个函数中移除老的controller的监听,并创建新controller的监听。
组件移除
组件移除,例如页面销毁的时候会依次执行:deactivate > dispose
deactivate
Called when this object is removed from the tree.
在dispose之前,会调用这个函数。实测在组件课件状态变化的时候会调用,当组件卸载时也会先一步dispose调用。
dispose
Called when this object is removed from the tree permanently.
调用次数:1次
一旦到这个阶段,组件就要被销毁了,这个函数一般会移除监听,清理环境。
reassemble
hot reload调用
|
名称
|
状态
|
|
initState
|
插入渲染树时调用,只调用一次
|
|
didChangeDependencies
|
state依赖的对象发生变化时调用
|
|
didUpdateWidget
|
组件状态改变时候调用,可能会调用多次
|
|
build
|
构建Widget时调用
|
|
deactivate
|
当移除渲染树的时候调用
|
|
dispose
|
组件即将销毁时调用
|
实际场景
假设我们从A页面跳转到B页面, 那么A,B页面的生命周期会是怎样的呢?
B页面进入初始化状态,依次执行4个函数:构造函数 > initState > didChangeDependencies > Widget build , 此时页面加载完成,进入运行态。
此时A页面依次执行deactivate > build函数。注意 此时A页面并未卸载。
然后我们假设B页面只有一个按钮,点击B页面中的按钮,改变按钮的文字,会执行widget的build方法 ,(理论上也应该执行didUpdateWidget,但我这里没有)。
这时,我们点击返回键从B页面返回到A页面。
A页面重新显示,B页面开始卸载。
那么A先执行deactivate > build , 然后B页面依次执行:deactivate > dispose 。
此时A页面进入运行态,B页面移除。
本次示例B页面代码:
/*
* Created by 李卓原 on 2018/9/13.
* email: zhuoyuan93@gmail.com
*
*/
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class NewsDetailPage extends StatefulWidget {
@override
State<StatefulWidget> createState() => NewsDetailState();
}
class NewsDetailState extends State<NewsDetailPage> {
int text = 1;
NewsDetailState() {
print('构造函数');
}
@override
void initState() {
print('init state');
super.initState();
}
@override
void didChangeDependencies() {
print('didChangeDependencies');
super.didChangeDependencies();
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
print('widget build');
return Scaffold(
body: Center(
child: _loading(),
),
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('咨询详情'),
),
);
}
@override
void didUpdateWidget(NewsDetailPage oldWidget) {
print('组件状态改变:didUpdateWidget');
super.didUpdateWidget(oldWidget);
}
@override
void deactivate() {
print('移除时:deactivate');
super.deactivate();
}
@override
void dispose() {
print('移除时:dispose');
super.dispose();
}
//预加载布局
Widget _loading() {
return Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
CircularProgressIndicator(
strokeWidth: 1.0,
),
Container(
child: Text("正在加载"),
margin: EdgeInsets.only(top: 10.0),
)
],
);
}
}
Tips:
下面内容来自咸鱼技术团队.
当ListView中的item滚动出可显示区域的时候,item会被从树中remove掉,此item子树中所有的state都会被dispose,state记录的数据都会销毁,item滚动回可显示区域时,会重新创建全新的state、element、renderobject使用hot reload功能时,要特别注意state实例是没有重新创建的,如果该state中存在一下复杂的资源更新需要重新加载才能生效,那么需要在reassemble()添加处理,不然当你使用hot reload时候可能会出现一些意想不到的结果,例如,要将显示本地文件的内容到屏幕上,当你开发过程中,替换了文件中的内容,但是hot reload没有触发重新读取文件内容,页面显示还是原来的旧内容.idChangeDependencies有两种情况会被调用。创建时候在initState 之后被调用在依赖的InheritedWidget发生变化的时候会被调用正常的退出流程中会执行deactivate然后执行dispose。但是也会出现deactivate以后不执行dispose,直接加入树中的另一个节点的情况。这里的状态改变包括两种可能:1.通过setState内容改变2.父节点的state状态改变,导致孩子节点的同步变化。
App生命周期
需要指出的是如果想要知道App的生命周期,那么需要通过WidgetsBindingObserver的didChangeAppLifecycleState 来获取。通过该接口可以获取是生命周期在AppLifecycleState类中。常用状态包含如下几个:
|
名称
|
状态
|
|
resumed
|
可见并能响应用户的输入
|
|
inactive
|
处在并不活动状态,无法处理用户响应
|
|
paused
|
不可见并不能响应用户的输入,但是在后台继续活动中
|
一个实际场景中的例子:
在不考虑suspending的情况下:
从后台切入前台生命周期变化如下: AppLifecycleState.inactive->AppLifecycleState.resumed;
从前台压后台生命周期变化如下: AppLifecycleState.inactive->AppLifecycleState.paused;
本文主要梳理一下StatefulWidget和StatelessWidget的生命周期

微组件
StatelessWidget
-
接收外部数据
-
执行部件构造方法
-
当传入数据改变时会重新渲染UI
StatefulWidget
-
接收外部数据
-
执行部件构造方法和状态初始化方法
-
当传入数据和 本类数据改变时都会重新渲染UI

-
ProductsManager部件初始化
-
创建ProductsManagerState
-
调用ProductsManagerState中的initState方法
-
ProductsManagerState渲染
-
Products部件初始化
-
Products渲染
当点击add product按钮数据发生改变时
1.数据_products发生了变化 通过setState方法通知数据发生了改变 ProductsManagerState build方法被调用 -
而Products进行了重新构造,也就是说当外部数据变化时 Products中的 _products 直接被替换成传入的新数据而不是在修改原有数据

flutter拥有类似于react-native的状态机刷新机制,得益于分离出了StatelessWidget和StatefulWidget,资源分配更加合理的了,代码思路也清晰很多.
lutter中的视图Widget像Android中的Activity一样存在生命周期,生命周期的回调函数体都在State中。
组件State的生命周期整理:
创建阶段
Log所示:

image.png
Widget状态改变
操作:横竖屏切换
Log所示:
其他生命周期并没有执行
竖屏切换到横屏执行2次
横屏切换到竖屏执行2次
Log所示:
其他生命周期并没有执行
竖屏切换到横屏执行2次
横屏切换到竖屏执行2次

image.png
App切后台,再切回来
Log所示:

image.png
销毁阶段
Log所示:

image.png
流程如图:

image.png
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class LifecycleAppPage extends StatefulWidget {
@override
State<StatefulWidget> createState() {
return new _LifecycleAppPageState('构造函数');
}
}
class _LifecycleAppPageState extends State<LifecycleAppPage>
with WidgetsBindingObserver {
String str;
int count = 0;
_LifecycleAppPageState(this.str);
@override
void initState() {
print(str);
print('initState');
super.initState();
WidgetsBinding.instance.addObserver(this);
}
@override
void didChangeDependencies() {
print('didChangeDependencies');
super.didChangeDependencies();
}
@override
void didUpdateWidget(LifecycleAppPage oldWidget) {
print('didUpdateWidget');
super.didUpdateWidget(oldWidget);
}
@override
void deactivate() {
print('deactivate');
super.deactivate();
}
@override
void dispose() {
print('dispose');
WidgetsBinding.instance.removeObserver(this);
super.dispose();
}
@override
void didChangeAppLifecycleState(AppLifecycleState state) {
switch (state) {
case AppLifecycleState.inactive:
print('AppLifecycleState.inactive');
break;
case AppLifecycleState.paused:
print('AppLifecycleState.paused');
break;
case AppLifecycleState.resumed:
print('AppLifecycleState.resumed');
break;
case AppLifecycleState.suspending:
print('AppLifecycleState.suspending');
break;
}
super.didChangeAppLifecycleState(state);
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
print('build');
return new Scaffold(
appBar: new AppBar(
title: new Text('lifecycle 学习'),
centerTitle: true,
),
body: new OrientationBuilder(
builder: (context, orientation) {
return new Center(
child: new Text(
'当前计数值:$count',
style: new TextStyle(
color: orientation == Orientation.portrait
? Colors.blue
: Colors.red),
),
);
},
),
floatingActionButton: new FloatingActionButton(
child: new Text('click'),
onPressed: () {
count++;
setState(() {});
}),
);
}
}
class LifecyclePage extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// TODO: implement build
return new Scaffold(
body: new LifecycleAppPage(),
);
}
}
6 of 7 in the series: Fltter移动开发相关
- sqflite操作相关

- TextField多行操作

- 免费作图工具

- Flutter环境更新方法
- 实体类自动生成工具的配置

实体类自动生成工具的配置
- 理解Flutter widget的生命周期

- 按钮扁平化用法示例-buildFlatButton

按钮扁平化用法示例-buildFlatButton
TextField多行操作
new TextField(
keyboardType: TextInputType.multiline,
maxLines: whatever,
2 of 7 in the series: Fltter移动开发相关
- sqflite操作相关

- TextField多行操作

- 免费作图工具

- Flutter环境更新方法
- 实体类自动生成工具的配置

实体类自动生成工具的配置
- 理解Flutter widget的生命周期

- 按钮扁平化用法示例-buildFlatButton

按钮扁平化用法示例-buildFlatButton
sqflite操作相关
SQLite 插件 同时支持 iOS 和Android.
-
-
支持事务和批处理
-
-
-
版本开放自动管理
-
-
-
增删改查助手
-
-
iOS 和 Android的后台线程中执行的DB操作
开始
在您的flutter项目中添加依赖项:
dependencies: ... sqflite: any
引用示例
Import
sqflite.dartimport 'package:sqflite/sqflite.dart';
原始的Sql查询
执行原始SQL查询的示例代码
// Get a location using getDatabasesPath
var databasesPath = await getDatabasesPath();
String path = join(databasesPath, 'demo.db');
// Delete the database
await deleteDatabase(path);
// open the database
Database database = await openDatabase(path, version: 1,
onCreate: (Database db, int version) async {
// When creating the db, create the table
await db.execute(
'CREATE TABLE Test (id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY, name TEXT, value INTEGER, num REAL)');
});
// Insert some records in a transaction
await database.transaction((txn) async {
int id1 = await txn.rawInsert(
'INSERT INTO Test(name, value, num) VALUES("some name", 1234, 456.789)');
print('inserted1: $id1');
int id2 = await txn.rawInsert(
'INSERT INTO Test(name, value, num) VALUES(?, ?, ?)',
['another name', 12345678, 3.1416]);
print('inserted2: $id2');
});
// Update some record
int count = await database.rawUpdate(
'UPDATE Test SET name = ?, VALUE = ? WHERE name = ?',
['updated name', '9876', 'some name']);
print('updated: $count');
// Get the records
List<Map> list = await database.rawQuery('SELECT * FROM Test');
List<Map> expectedList = [
{'name': 'updated name', 'id': 1, 'value': 9876, 'num': 456.789},
{'name': 'another name', 'id': 2, 'value': 12345678, 'num': 3.1416}
];
print(list);
print(expectedList);
assert(const DeepCollectionEquality().equals(list, expectedList));
// Count the records
count = Sqflite
.firstIntValue(await database.rawQuery('SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Test'));
assert(count == 2);
// Delete a record
count = await database
.rawDelete('DELETE FROM Test WHERE name = ?', ['another name']);
assert(count == 1);
// Close the database
await dat
SqlHelper(助手)
使用助手的示例
inal String tableTodo = 'todo';
final String columnId = '_id';
final String columnTitle = 'title';
final String columnDone = 'done';
class Todo {
int id;
String title;
bool done;
Map<String, dynamic> toMap() {
var map = <String, dynamic>{
columnTitle: title,
columnDone: done == true ? 1 : 0
};
if (id != null) {
map[columnId] = id;
}
return map;
}
Todo();
Todo.fromMap(Map<String, dynamic> map) {
id = map[columnId];
title = map[columnTitle];
done = map[columnDone] == 1;
}
}
class TodoProvider {
Database db;
Future open(String path) async {
db = await openDatabase(path, version: 1,
onCreate: (Database db, int version) async {
await db.execute('''
create table $tableTodo (
$columnId integer primary key autoincrement,
$columnTitle text not null,
$columnDone integer not null)
''');
});
}
Future<Todo> insert(Todo todo) async {
todo.id = await db.insert(tableTodo, todo.toMap());
return todo;
}
Future<Todo> getTodo(int id) async {
List<Map> maps = await db.query(tableTodo,
columns: [columnId, columnDone, columnTitle],
where: '$columnId = ?',
whereArgs: [id]);
if (maps.length > 0) {
return Todo.fromMap(maps.first);
}
return null;
}
Future<int> delete(int id) async {
return await db.delete(tableTodo, where: '$columnId = ?', whereArgs: [id]);
}
Future<int> update(Todo todo) async {
return await db.update(tableTodo, todo.toMap(),
where: '$columnId = ?', whereArgs: [todo.id]);
}
Future close() async => db.close();
}
Transaction
不要使用数据库,而只在事务中使用Transaction对象来访问数据库
await database.transaction((txn) async {
// Ok
await txn.execute('CREATE TABLE Test1 (id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY)');
// DON'T use the database object in a transaction
// this will deadlock!
await database.execute('CREATE TABLE Test2 (id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY)');
});
批处理支持
为了避免频繁的交互,可以使用Batch:
batch = db.batch();
batch.insert('Test', {'name': 'item'});
batch.update('Test', {'name': 'new_item'}, where: 'name = ?', whereArgs: ['item']);
batch.delete('Test', where: 'name = ?', whereArgs: ['item']);
results = await batch.commit();
获取每个操作的结果都会带来成本(插入的id和更新和删除的更改的数量),尤其是在执行额外SQL请求的Android上。如果不关心结果并担心消耗大量资源和性能,可以使用
await batch.commit(noResult: true);
警告,在事务期间,在提交事务之前不会提交批处理
wait database.transaction((txn) async {
var batch = txn.batch();
// ...
// commit but the actual commit will happen when the transaction is commited
// however the data is available in this transaction
await batch.commit();
// ...
});
默认情况下,一遇到错误(通常恢复未提交的更改),批处理就停止。您可以忽略错误,即使碰到一个操作失败,也能运行和提交操作成功每个提交:
await batch.commit(continueOnError: true);
表和列名
一般来说,最好避免对实体名称使用SQLite关键字。如果使用下列名称中的任何一个:
"add","all","alter","and","as","autoincrement","between","case","check",
"collate","commit","constraint","create","default","deferrable","delete",
"distinct","drop","else","escape","except","exists","foreign","from",
"group","having","if","in","index","insert","intersect","into","is",
"isnull","join","limit","not","notnull","null","on","or","order",
"primary","references","select","set","table","then","to",
"transaction","union","unique","update","using","values","when","where"
助手会逃避这个名字,如。。
db.query('table')
以上这行代码将等同于手动在表名周围添加双引号(令人困惑的是,这里命名的表),等同于如下代码
db.rawQuery('SELECT * FROM "table"');
但是在任何其他原始语句(包括order.、where、group.)中,确保使用双引号正确地转义名称。例如,参见下面,列名组在列参数中没有转义,而是在where参数中转义。
db.query('table', columns: ['group'], where: '"group" = ?', whereArgs: ['my_group']);
SQLite 支持的数据类型
Sqlite还没有对值进行有效性检查,因此请避免不支持的类型
DateTime
SQLite不支持DateTime类型。我个人将它们存储为int(.sSinceEpoch)或string(iso8601)
Bool
SQLite不支持bool类型。使用整数和0和1值。
INTEGER
-
-
Dart type:
int
-
-
取值范围: 从-2^63 到 2^63 – 1
REAL
-
Dart type:
num
TEXT
-
Dart type:
String
BLOB
-
-
Dart type:
Uint8List
-
-
Dart type
List<int>是支持的,但是不推荐使用 慢速转换)
当前问题
-
-
Due to the way transaction works in SQLite (threads), concurrent read and write transaction are not supported. All calls are currently synchronized and transactions block are exclusive. I thought that a basic way to support concurrent access is to open a database multiple times but it only works on iOS as Android reuses the same database object. I also thought a native thread could be a potential future solution however on android accessing the database in another thread is blocked while in a transaction…
-
-
Currently INTEGER are limited to -2^63 to 2^63 – 1 (although Android supports bigger ones)
上述机翻由于事务在SQLIT(线程)中的工作方式,不支持并发读写事务。所有调用当前都是同步的,事务块是独占的。我认为支持并发访问的基本方法是多次打开数据库,但是它只能在iOS上工作,因为Android重用了相同的数据库对象。我还认为本机线程可能是未来可能的解决方案,但是当android访问另一个线程中的数据库时,在事务中会阻塞……目前INTEGER被限制在-2^63到2^63-1(尽管Android支持更大的)
更多
相关类库
by phoenix翻译,原文转自
1 of 7 in the series: Fltter移动开发相关
- sqflite操作相关

- TextField多行操作

- 免费作图工具

- Flutter环境更新方法
- 实体类自动生成工具的配置

实体类自动生成工具的配置
- 理解Flutter widget的生命周期

- 按钮扁平化用法示例-buildFlatButton

按钮扁平化用法示例-buildFlatButton
实体类自动生成工具的配置
1.实体类自动生成
a.在线实体类处自动生成
1).JsonToDartClass转换地址-1:
2).JsonToDartClass转换地址-2:
b.离线实体类自动生成工具
Formatter是开源的,项目地址;https://github.com/debuggerx01/JSONFormat4Flutter
2.使用工程自动生成代码
参考资料
操作步骤
-
-
工程依赖中加入依赖库
dependencies: cupertino_icons: ^0.1.2 fluttertoast: ^2.0.3 json_annotation: ^1.2.0 dev_dependencies: build_runner: ^0.10.1+1 json_serializable: ^1.1.0
-
-
-
建立需要生成的实体类
import 'package:json_annotation/json_annotation.dart'; part 'User.g.dart'; @JsonSerializable() class User { User(this.id, this.username, ... ); String username; 。。。 factory User.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) => _$UserFromJson(json); Map<String, dynamic> toJson() => _$UserToJson(this); // 命名构造函数 User.empty(); }
-
-
在控制台输入生成命令
flutter packages pub run build_runner build
5 of 7 in the series: Fltter移动开发相关
- sqflite操作相关

- TextField多行操作

- 免费作图工具

- Flutter环境更新方法
- 实体类自动生成工具的配置

实体类自动生成工具的配置
- 理解Flutter widget的生命周期

- 按钮扁平化用法示例-buildFlatButton

按钮扁平化用法示例-buildFlatButton
Flutter环境更新方法
常规更新方法:
运行:flutter upgrade,然后等待自动更新完成即可,
非常贵更新方法:
1.更新flutter代码库
找到flutter库的安装目录,运行git,同步拉取到最新的代码,
2.更新依赖
运行flutter doctor -v 自动下载更新依赖的库
Microsoft Windows [版本 10.0.17134.112]
(c) 2018 Microsoft Corporation。保留所有权利。
F:\JavaWorker\deheng\android\hemodialysis>flutter doctor -v
Checking Dart SDK version...
Downloading Dart SDK from Flutter engine 72c7a7567228cdaf8b7aa4a9e3d212ef9d4cc0ed...
Unzipping Dart SDK...
Building flutter tool...
Running pub upgrade...
Downloading package sky_engine... 1.1s
Downloading common tools... 2.6s
Downloading windows-x64 tools... 5.9s
Downloading android-arm-profile/windows-x64 tools... 1.2s
Downloading android-arm-release/windows-x64 tools... 0.8s
Downloading android-arm64-profile/windows-x64 tools... 0.9s
Downloading android-arm64-release/windows-x64 tools... 0.9s
Downloading android-x86 tools... 4.8s
Downloading android-x64 tools... 4.9s
Downloading android-arm tools... 3.4s
Downloading android-arm-profile tools... 1.8s
Downloading android-arm-release tools... 2.2s
Downloading android-arm64 tools... 1.9s
Downloading android-arm64-profile tools... 1.8s
Downloading android-arm64-release tools... 1.5s
Downloading android-arm-dynamic-profile tools... 1.9s
Downloading android-arm-dynamic-release tools... 2.8s
Downloading android-arm64-dynamic-profile tools... 2.0s
Downloading android-arm64-dynamic-release tools... 1.7s
[√] Flutter (Channel beta, v0.10.3-pre.3, on Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.17134.112], locale zh-CN)
• Flutter version 0.10.3-pre.3 at F:\ProgramFiles\flutter
• Framework revision 233435c02a (42 minutes ago), 2018-11-30 10:00:27 +0800
• Engine revision 72c7a75672
• Dart version 2.1.0 (build 2.1.0-dev.9.4 f9ebf21297)
[√] Android toolchain - develop for Android devices (Android SDK 28.0.3)
• Android SDK at F:\ProgramFiles\android\sdk
• Android NDK location not configured (optional; useful for native profiling support)
• Platform android-28, build-tools 28.0.3
• ANDROID_HOME = F:\ProgramFiles\android\sdk
• Java binary at: F:\ProgramFiles\android\Android Studio\jre\bin\java
• Java version OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_152-release-1136-b06)
• All Android licenses accepted.
[√] Android Studio (version 3.2)
• Android Studio at F:\ProgramFiles\android\Android Studio
• Flutter plugin version 31.1.1
• Dart plugin version 181.5656
• Java version OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_152-release-1136-b06)
[√] IntelliJ IDEA Ultimate Edition (version 2018.2)
• IntelliJ at F:\ProgramFiles\JetBrains\IntelliJ IDEA 2018.2.4
• Flutter plugin version 30.0.2
• Dart plugin version 182.5124
[√] Connected device (2 available)
• MI PAD 4 • 6074f4a0 • android-arm64 • Android 8.1.0 (API 27)
• Che1 CL20 • f4e3fb7f933b • android-arm • Android 4.4.4 (API 19)
• No issues found!
F:\JavaWorker\deheng\android\hemodialysis>
4 of 7 in the series: Fltter移动开发相关
- sqflite操作相关

- TextField多行操作

- 免费作图工具

- Flutter环境更新方法
- 实体类自动生成工具的配置

实体类自动生成工具的配置
- 理解Flutter widget的生命周期

- 按钮扁平化用法示例-buildFlatButton

按钮扁平化用法示例-buildFlatButton